It is Real and Has an Identifiable Biological Basis Several published peer-reviewed studies conducted by the Johns Hopkins Lyme Disease Research Center are generating a growing body of evidence that […]
Lyme Disease Research
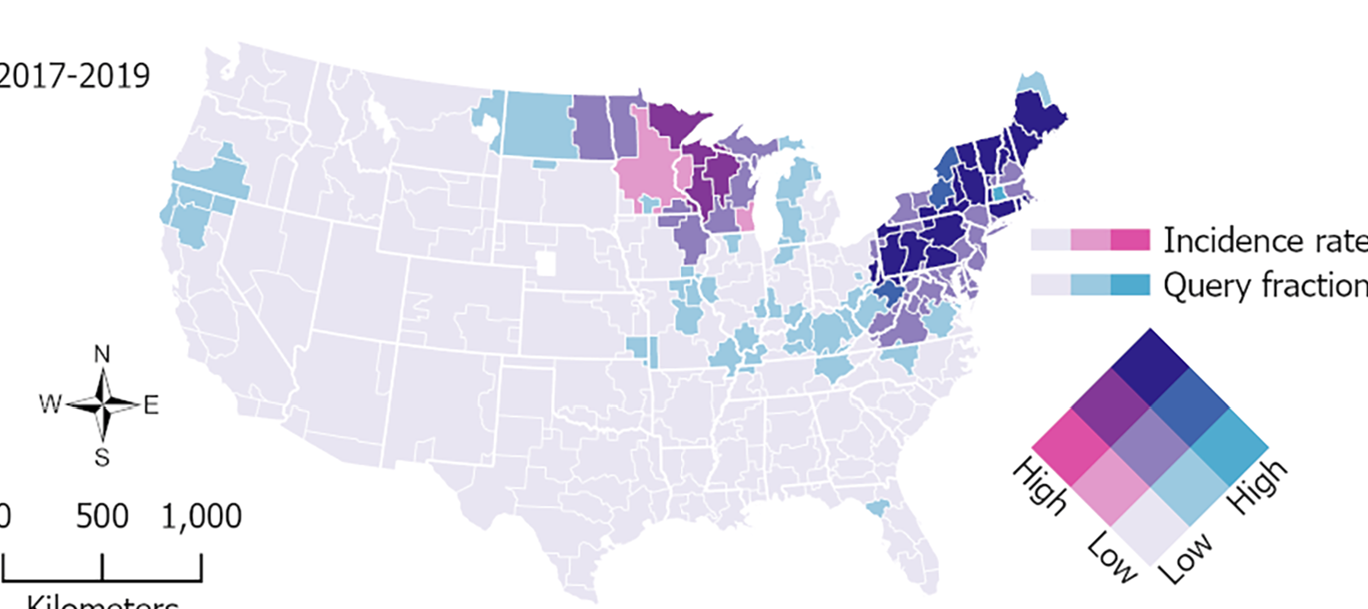
Identifying the Geographic Leading Edge of Lyme Disease Using Google Health Trends
Invalidation by Medical Professionals in Post-Treatment Lyme Disease
Risk of post-treatment Lyme disease in patients with early diagnosed and promptly treated Lyme disease: A prospective cohort study
Predicting Lyme Disease from Patients’ Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Profiled with RNA-Sequencing

This study uses total RNA-sequencing of Lyme disease patients’ peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Using novel data analysis approaches, three unique groups of Lyme disease patients were identified, each with characteristic clinical and immunological features. Data from healthy controls and COVID-19 patients were included. Using machine learning classifiers, the study shows that Lyme patients can be distinguished from healthy controls as well as from COVID-19 patients.